Describe Atp Synthase and Its Role
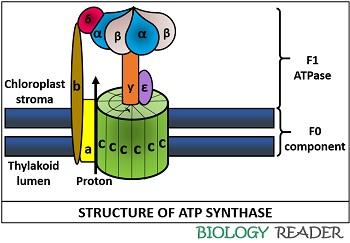
ATP synthase is a complex structure consisting of two domains F O and F 1. Describe the Quaternary structure of ATP synthase identify each subunit and its function in this enzyme.
Atp Synthesis Encyclopedia Of The Environment
What is role of H gradient.
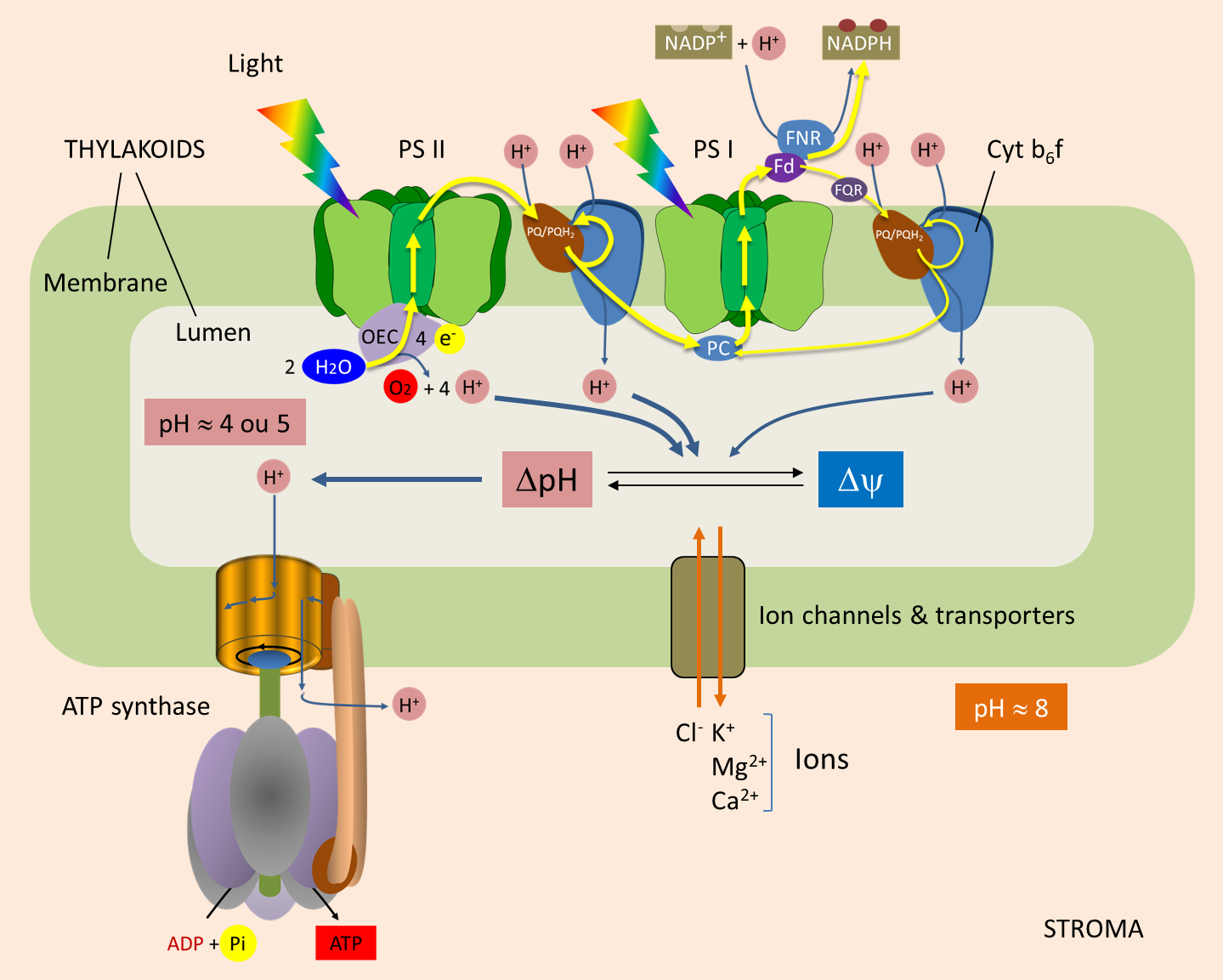
. The role of ATP synthase in photosynthesis is to transports a proton down the gradient and uses the energy to complete the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. -ATP synthase is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria Function-ATP synthase combines with ADP in order to form ATP-ATP is needed to power all cellular processes-ATP synthase function is to produce ATP. The mitochondrial H -ATP synthase is a primary hub of cellular homeostasis by providing the energy required to sustain cellular activity and regulating the production of signaling molecules that reprogram nuclear activity needed for adaption to changing cues.
ATP synthase is an enzyme that plays a vital role in the addition of a phosphate to ADP or adenosine diphosphate to form ATP or adenosine triphosphate. Up to 24 cash back It is a hollow shape with a pathway in its center that enables protons to flow across the membrane into the mitochondrial matrix or thylakoid lumen. ATP is the principal.
This energy is broken down and used for various cell processes. ATP is mainly produced in the mitochondria and is an important enzyme that provides energy for the cell to use through the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate ATP. And ATP synthase provides a channel for those protons.
As protons move across the membrane as facilitated by ATP synthase energy is produced. Describe the Quaternary structure of ATP synthase identify each subunit and its function in this enzyme. ATP synthase forms ATP from adenosine diphosphate ADP and an inorganic phosphate Pi through oxidative phosphorylation which is a process in which enzymes oxidize nutrients to form ATP.
Modification of work by Klaus Hoffmeier Dinitrophenol DNP is an uncoupler that makes the inner mitochondrial membrane leaky to protons. The enzyme is located within the mitochondria of a cell where the synthesis of ATP occurs. Answer 1 of 3.
Discuss the source fate and flow of electrons and energy in. ATP synthase Enzyme that synthesizes ATP. Eg 13 bisphosphoglycerate to 3 phosphoglycerate yield ATP directly by.
ATP synthase is an enzyme located in the mitochondria and chloroplasts plant cells that produces the energy currency of the cell known as adenosine triphosphate ATP. Its primary role is to produce high energy ATP molecule. An enzyme is a protein that helps biochemical reactions occur.
ATP synthase is a protein that synthesizes adenosine diphosphate ADP and an extra phosphate together into adenosine triphosphate ATP. The role of ATP in metabolism is phosphorylation where a phosphate PO4 group is transferred from ATP to another molecule. The ATP synthase or F 1 F 0 ATPase and also referred to as complex V uses the free energy of an electrochemical gradient of protons or sodium ions generated by the respiratory chain to synthesize ATP.
This energy is used to catalyze the formation of ATP by ATP synthase hence its namesake through the. Substrate level phosphorylation is that ATP synthesis occurs whan an enzyme directly transfer phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP. But as those protons travel through the ATP synthase they turn this part of it which drives this axle and then this axle nudges these parts of the protein so that they jam together an ADP with a phosphate group to produce ATP.
Photosynthesis starts with the absorption of light or solar energy by the plant pigments called chlorophyll. Science Biology QA Library Describe in detail the role of ATP synthase in the thylakoid membrane. ATP synthase is a complex molecular machine that uses a proton H gradient to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate Pi.
The role of ATP synthase is to release energy that was stored in the ATP molecule. ATP synthase is a transmembrane enzyme complex which catalyses the generation of ATP through the condensation of ADP plus Pi. It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation of P-O bond phosphodiester bond.
F 1 is a spherical structure sticks out into the matrix and is anchored to the membrane consists of three α- and three β- subunits all of which can bind nucleotides but only the β-subunits can take part in the reactions Fig. ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate ATP using adenosine diphosphate ADP and inorganic phosphate P i. In doing so the potential energy of that molecule is increased enabling its participation in further biochemical transformations that were not energetica.
It was used until 1938 as a weight-loss drug. ATP synthase is an enzyme that directly generates adenosine triphosphate ATP during the process of cellular respiration. ATP synthase brings out the formation of ATP at the time of light-reaction photosynthesis.
What is the role of the proteins ATP synthase. ATP synthase is a membrane protein which converts the proton gradient across membrane into energy storing molecule ATP important for biological purposes. Discuss the source fate and flow of electrons and energy in detail naming all molecules.
ATP is used by most all. ATP synthase is a molecular machine. ATP synthase catalyzes the reaction to combine ADP or adenosine diphosphate with a single phosphate unit to yield ATP.
The ATP synthases comprise a very large group of highly conserved enzymes that are found in the bacterial cytoplasmic membranes the thylakoid membranes of. ATP synthase is an enzyme that synthesizes adenosine triphosphate ATP in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
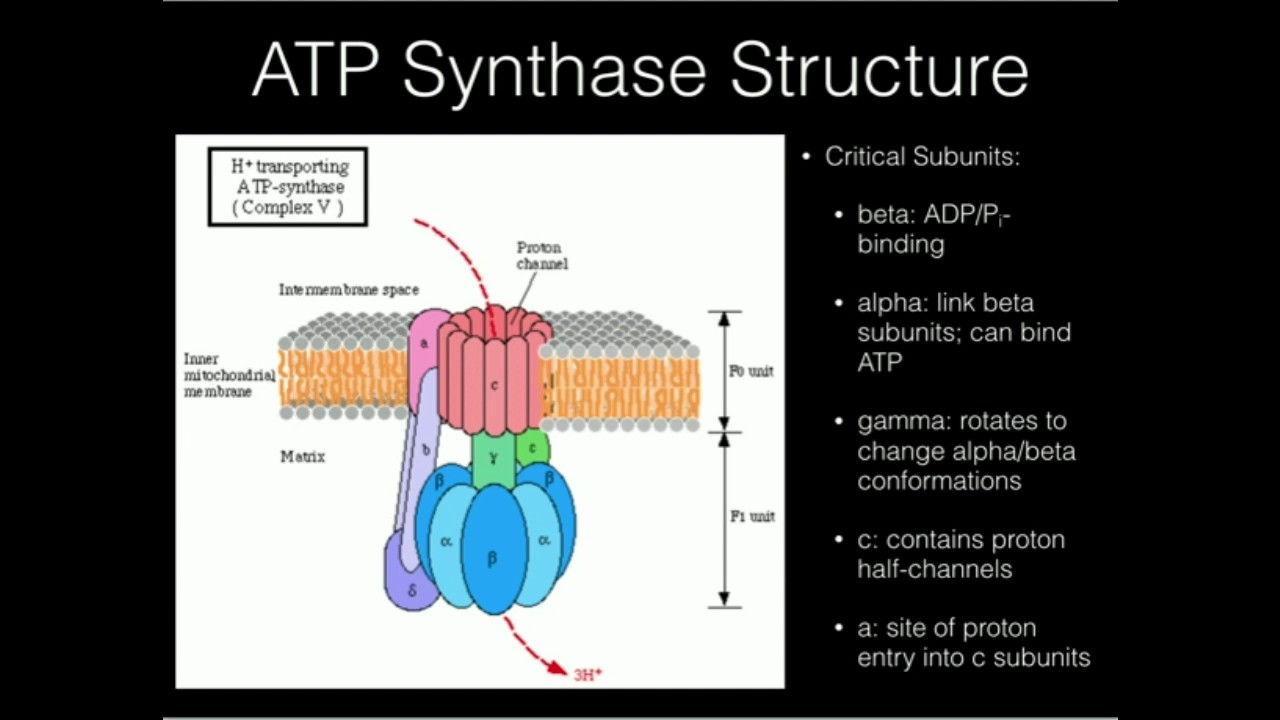
Atp Synthase Mechanism Of Atp Synthesis Youtube

Atp Synthase In Photosynthesis Definition Structure Mechanism Biology Reader

Atp Synthase Definition Structure Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
No comments for "Describe Atp Synthase and Its Role"
Post a Comment